
The improved signal strength also facilitates the measurement of very small, low-scattering particles down to the lower nanometer range. This results in a much stronger measurement signal and allows the use of laser diodes as light source and silicon photodiodes as detector. In contrast, the signal intensity in the heterodyne measurement is proportional to i s x i 0, the product of the scattered intensity and intensity of the reference. This is proportional to i s 2, the mean scattered light intensity squared, in the homodyne measurement. The most important of these is signal intensity. Of the two approaches, the heterodyne mode with "controlled reference" offers many advantages over the homodyne setup in a dynamic light scattering analyzer. The resulting detector signal in both methods contains a distribution of frequencies that is representative of the size of the particles in suspension. In contrast to this, controlled reference, or heterodyne detection, superimposes the scattered light on a portion of the incident light, which provides the reference for determining the frequency shifts. In the homodyne approach, the scattered light itself provides the reference for determining the frequency shift. Two approaches exist for optical reference: homodyne detection (also called "self-beating" or "self-reference") and heterodyne detection ("reference beating" or "controlled reference"). In Dynamic Light Scattering, the shift frequencies are on the scale of 1 Hz to 100KHz, which can be easily measured. These shift frequencies can be determined by comparison with a coherent optical reference. Measured over time, motion causes a distribution of frequency shifts. The light scattered by the particles thus contains slight frequency shifts caused by the time-dependent position or velocity of the particles. The fluctuations are caused by the fact that the particles scattering the light move relative to each other, resulting in constantly changing interferences within the total scattered light. The temporal fluctuation of the scattered light signal is important here, because it contains information about the movement of the particles. The particles are illuminated with a monochromatic, coherent light source (laser) and the light scattered by the particles is recorded. The Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) technique measures motion optically by recording the scattered light signal at a fixed angle. Other advantages include measurements of both highly concentrated and highly dilute samples, and the ability to determine Zeta Potential, molecular weight and concentration, which is built into many analyzers. It is a technique suited to the analysis and characterization of nanoparticles.
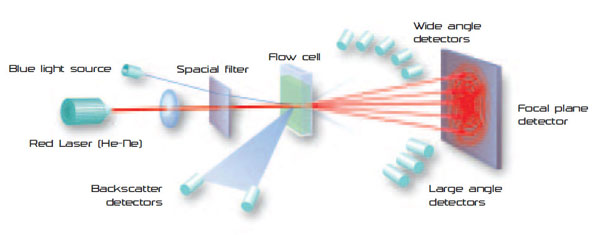
While Laser Diffraction (LD) often reaches its limits for particles smaller than 100 nm due to the weak signal and the low angular variance in scattering signal, this is where the strength of dynamic light scattering lies. The light scattered by particles contains information on the diffusion speed and thus on the size distribution.ĭynamic light scattering enables the analysis of particles in a size range from 0.3 nm to 10000 nm.
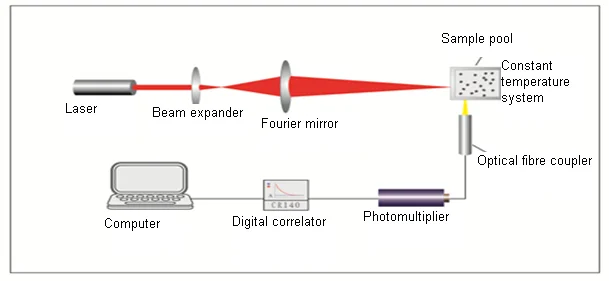
It is based on the Brownian motion of particles - this states that smaller particles move faster, while larger ones move slower in a liquid. TURBISCAN® is the solution to analyze particle size and stability of the samples in their native form.Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) is an established and precise measurement technique for characterizing particle sizes in suspensions and emulsions. Unlike most of the measurement techniques available, that require processing of the sample (pumping, dilution, stirring, centrifugation etc.), for instance: Laser Diffraction, Dynamic Light Scattering, Particle Tracking Analysis, Microscopy, Ultracentrifugation…. Actual dispersion state, such as the presence of agglomerates or flocs, can be rapidly and precisely identified and measured, without altering the real particle size. Thanks to the use of Static Multiple Light Scattering, no dilution or sample stress are required and the samples are analyzed in their original form. TURBISCAN® is a powerful tool to measure the mean particle size in concentrated media. Because particles or droplets are in weak equilibrium within the liquid phase, it is important to analyze their dispersion state in the native form. Particle size and its evolution are key parameters which have to be monitored and controlled to characterize formulation stability and aging over time. PARTICLE SIZE ANALYSIS IN NATIVE STATE DISPERSIONS


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
